Advanced Alumina Metallized Ceramic Ring / Tube for Gas Discharge
Basic Info.
| Model NO. | Customized |
| Further Finishing Treatment | Machining, Glazing, etc |
| Feature | High Performance and High Precision |
| Surface Metallization Process | Mo-Mn Method |
| Optional Purity | 94.4%-99.8% Alumina |
| Color | White, Beige, Pink |
| Product Name | Structural Ceramic Components with Metallization |
| Transport Package | Vacuum Packaging |
| Specification | As per the drawing |
| Trademark | JingHui |
| Origin | China |
| HS Code | 8547100000 |
| Production Capacity | 50000PCS/Month |
Packaging & Delivery
Package Size 36.00cm * 20.00cm * 24.00cm Package Gross Weight 10.000kgProduct Description
Advanced Alumina Metallized Ceramic Ring / Tube for Gas DischargeIntroduction to Ceramic Structural Parts
Ceramic structural parts are a general term for various complex-shaped ceramic parts.
Ceramic structural parts are made by selecting high-purity synthetic compounds (such as alumina, zirconia, silicon nitride, etc.), using forming method like dry pressing, hot pressing, isostatic pressing or injection molding, sintering at high temperature, and finally performing precision machining.
What are the Advantages of Ceramic Structural Parts?
Ceramic structural parts have high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, insulation and other properties, and can work well in various harsh environments.
Production Process
Our product production is mainly divided into 3 steps, forming - finishing - metallization. The production flow chart is shown below.
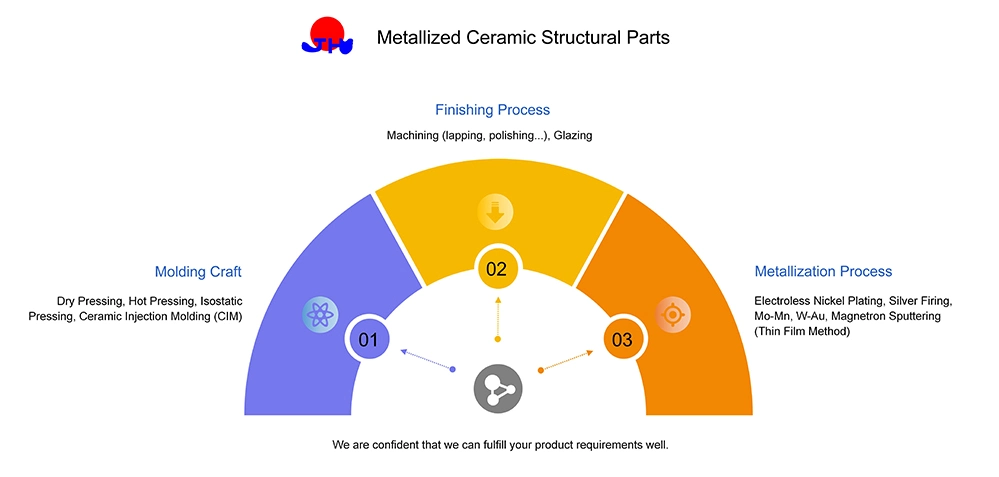
1. Forming Method
There are mainly Dry Pressing, Hot Pressing, Isostatic Pressing, and Ceramic Injection Molding (CIM), each of which has its own advantages and disadvantages. We will choose the most suitable forming method on the basis of saving costs and ensuring quality.
2. Finishing Process
In order to achieve the precision of the product, most ceramic structural parts need further finishing treatment after the sintering process. The main finishing processes we use are machining (lapping, polishing...) and glazing.
3. Metallization Process
Metallization of ceramics refers to the creation of thin metal layers (films) on the surface of ceramics. After the surface of the ceramic material is metallized, it has both the characteristics of ceramics and the properties of metal.
Which Metallization Processes We Support?
Jinghui specializes in the production of metallized ceramic structural components, has rich experience in manufacturing precision ceramic parts, and is proficient in the surface metallization process of ceramic structural parts such as Mo-Mn method, electroless nickel plating method, silver firing method and W-Au method. Here we focus on the Mo-Mn method.
Introduction to Mo-Mn MethodThe process of the Mo-Mn method is to coat a layer of metal powder (with Mo powder and Mn powder as the main raw materials) on the ceramic surface, and form a solidified and dense metallized layer through high-temperature sintering, thereby realizing the metallization of ceramics.
The brief process of Mo-Mn method is shown in the picture below.
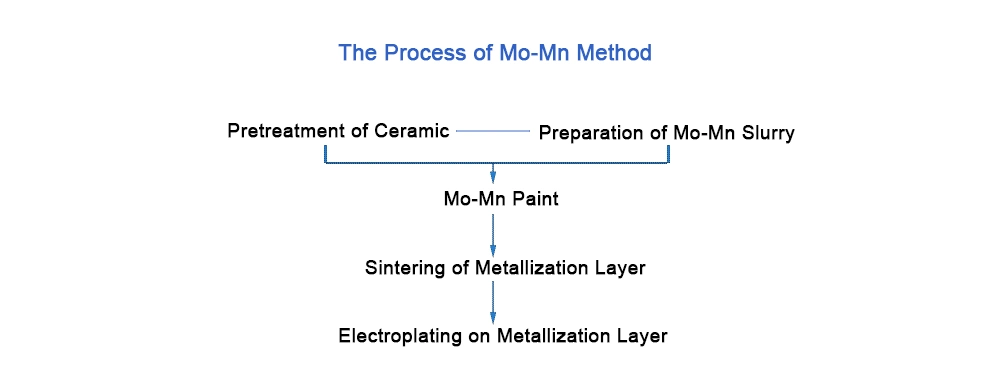
Metallized ceramic structural parts obtained by the Mo-Mn method have the following characteristics:1. High bonding strength, high air tightness, high reliability and good heat resistance.2. The finished product has dual characteristics of ceramic and metal.We can produce metallized ceramic structural parts of various specifications according to customers' drawings.Product Applications
Ceramic structural parts are widely used in semiconductor, optical fiber communication, laser, medical, equipment, petroleum, metallurgy, electronics and other industries.
We can produce products with different precision and complex structure according to customers' requirements.
Product Parameters
The following is the material properties of our alumina ceramic structural parts.
| Category | Property | Unit | 99.8%Al2O3 | 99.5%Al2O3 | 99%Al2O3 | 95%Al2O3 | 94.4%Al2O3 |
| Mechanical | Density | g/cm3 | ≥3.95 | ≥3.90 | ≥3.85 | ≥3.65 | ≥3.60 |
| Water absorption | % | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Vickers hardness | HV | 1700 | 1700 | 1700 | 1500 | 1500 | |
| Flexural strength | Mpa | ≥ 390 | ≥ 379 | ≥ 338 | ≥ 320 | ≥ 312 | |
| Compressive strength | Mpa | ≥ 2650 | ≥ 2240 | ≥ 2240 | ≥ 2000 | ≥ 2000 | |
| Fracture toughness | Mpam1/2 | 4-5 | 4-5 | 4-5 | 3-4 | 3-4 | |
| Thermal | Max. Service temperature(non-loading) | ºC | 1750 | 1675 | 1600 | 1500 | 1500 |
| CTE (Coefficient of thermal expansion)20-800ºC | 1×10-6/ºC | 6.5-8.2 | 6.5-8.0 | 6.2-8.0 | 5.0-8.0 | 5.0-8.0 | |
| Thermal shock | T (ºC) | ≥ 200 | ≥ 200 | ≥ 200 | ≥ 220 | ≥ 220 | |
| Thermal conductivity25ºC | W/(m·k) | 31 | 30 | 29 | 24 | 22.4 | |
| Specific heat | 1×103J/(kg·k) | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.78 | |
| Electrical | Volume resistivity25ºC | ohm·cm | > 1×1014 | > 1×1014 | > 1×1014 | > 1×1014 | > 1×1014 |
| 300ºC | 1×1012 | 1×1012 | 8×1011 | 1012-1013 | 1012-1013 | ||
| 500ºC | 2×1012 | 5×1010 | 2×109 | 1×109 | 1×109 | ||
| Dielectric strength | KV/mm | 20 | 19 | 18 | 18 | 18 | |
| Dielectric constant (1Mhz) | (E) | 9.8 | 9.7 | 9.5 | 9.5 | 9.5 |
Product Recommendations
Thank you for your visit. We can produce and process various special-shaped and high-precision ceramic structural parts according to your requirements.
We are confident that we can fulfill your product requirements well. Welcome to order with drawings or samples, and look forward to becoming your reliable partner!
View More